Figure C7a.1 Models of centralized, decentralized, and distributed system
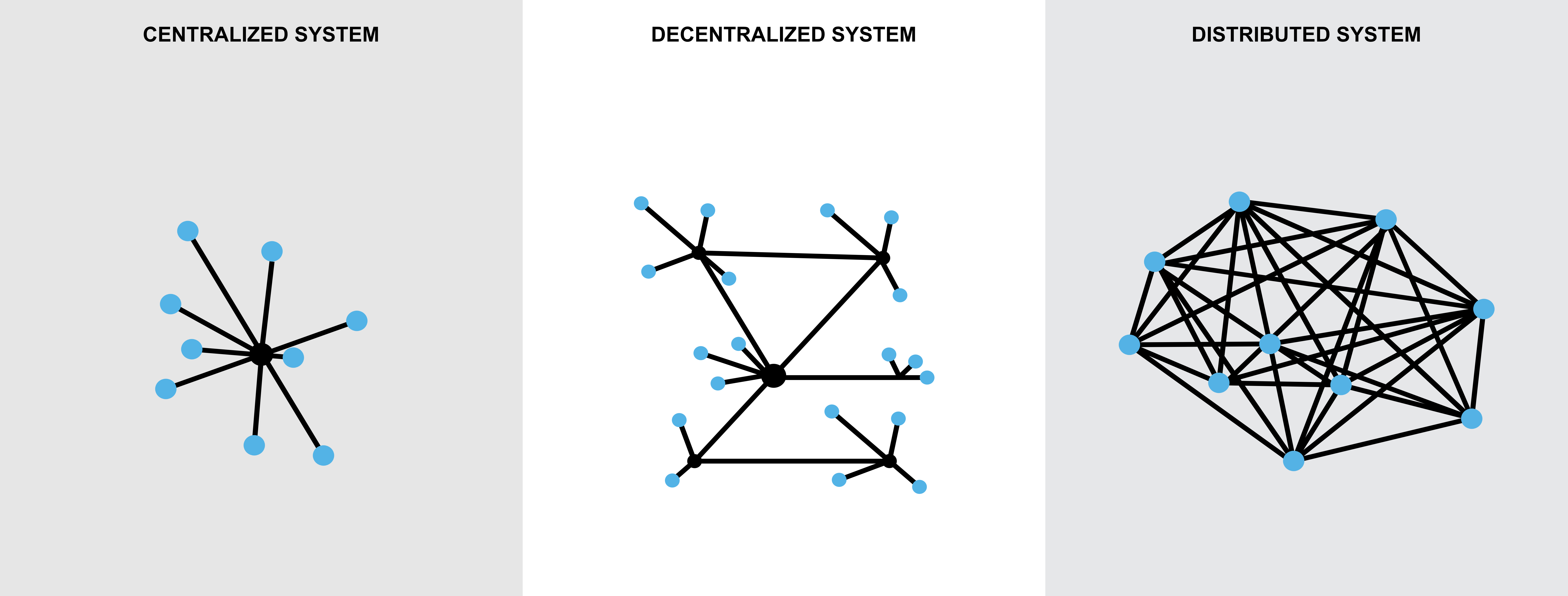
Centralize System
Centralized systems use client/server architecture where one or more client nodes are directly connected to a central server. It is the most used system in many states, private, services, and business organizations where a client sends a request to a company server and receives the response.
Decentralized System
A decentralized system is an interconnected state, private, services, and a business system where no single entity is the sole authority. For example, the Internet is a typical decentralized system in the information world.
Distributed System
Distribution is traditionally concerned with ensuring that products reach target customers directly and cost-effectively. In the case of services, distribution is principally concerned with access. Although distribution, as a concept, is relatively simple, in practice, distribution management may involve a diverse range of activities and disciplines, including detailed logistics, transportation warehousing, storage, inventory, management, and channel management, including a selection of channel members and rewarding distributors.
Three types of distribution channels are distinguished in the economy: wholesalers, retailers, and direct-to-consumer sales. Distribution is how total output, income, or wealth is distributed among individuals or the factors of production (such as labor, land, and capital).
Another example is the use of national accounts for classifying factor incomes and measuring their respective shares, as in national income or distribution of wealth and income, how the wealth and payment of a nation are divided among its population. The wealth and income of the world are divided among nations. And through the country to provinces and towns and villages.
The system theory knows the distribution function. It is a mathematical expression that describes the probability that a system will take on a specific value or set of values. For example, distribution is functional when you need to know which outcomes are most likely, the spread of potential deals, and the likelihood of different results.
Distribution involves doing the following things: Tracking the places where the product can be placed such that there is a maximum opportunity to buy it. Four distribution channels exist: direct selling, selling through intermediaries, dual distribution, and reverse logistics channels. The main objective of distribution is to make the flow of goods from production place to consumption place. For this, the role of the distribution channel system and its members becomes crucial.
In project management, distribution is a weighted average in which more weight is given to the most likely estimate. This alteration to the formula and placing more weight on the most reasonable estimate is made to increase the estimate's accuracy by making it follow the Normal Distribution shape. Project management knows two beta formals:
Triangular distribution: Triangular Distribution: E = (o + m + p) / 3 where E is Estimate; o = optimistic estimate; p = pessimistic estimate; m = most likely estimate.
Beta (or PERT): Beta Distribution (PERT): E = (o + 4m + p) / 6. The beta distribution is a weighted average in which more weight is given to the most likely estimate. This alteration to the formula and placing more weight on the most likely estimate is made to increase the estimate's accuracy by making it follow the Normal Distribution shape. Hence, in most cases, the Beta (PERT) distribution has been proven to be more accurate than the 3-Point triangular estimation. By using beta distribution, you can determine the level of certainty of this prediction. The variance is obtained by the difference between the pessimistic and the optimistic forecast divided by six squared. The variance is the square of the Standard deviation.
Note: Distribution means spreading the product throughout the marketplace so that many people can buy it. The statistical expression defines a Probability Density Function (PDF) Distribution as a statistical expression.
Distributed leadership covers internal and external cooperation in each SPC and among more SPCs to strengthen resilience, decipher vulnerability and protect the gender phenomenon of the Human on the global scale whether in a decentralized or centralized manner of leadership). The Self-Powered Community (SPC) model covers a landscape (a province) with about one million inhabitants anywhere where people now live.
People with similar interests organize joint events, prepare and implement projects on their territory in the community, and have common frameworks for their initiation and support. This environment receives, generates, and maintains a certain amount of data that characterizes society. The data are in stories about, read, and spread through local social activities, covering various topics.
Figure C7a.2 introduces the intersection scheme of the SPC Utility with the organization environment (micro, small and middle) and a filtered SED, DRR, and AH projects in two levels:
The upper level presents a network of standardized distribution units operating in the global market of the given service sector.
On a lower level, SPC Utility is a single distribution unit linked to the supply chains of products and services in a defined territory (one province).
The distribution mechanism focuses on working with information and data related to individual projects (see Chapters D and E).