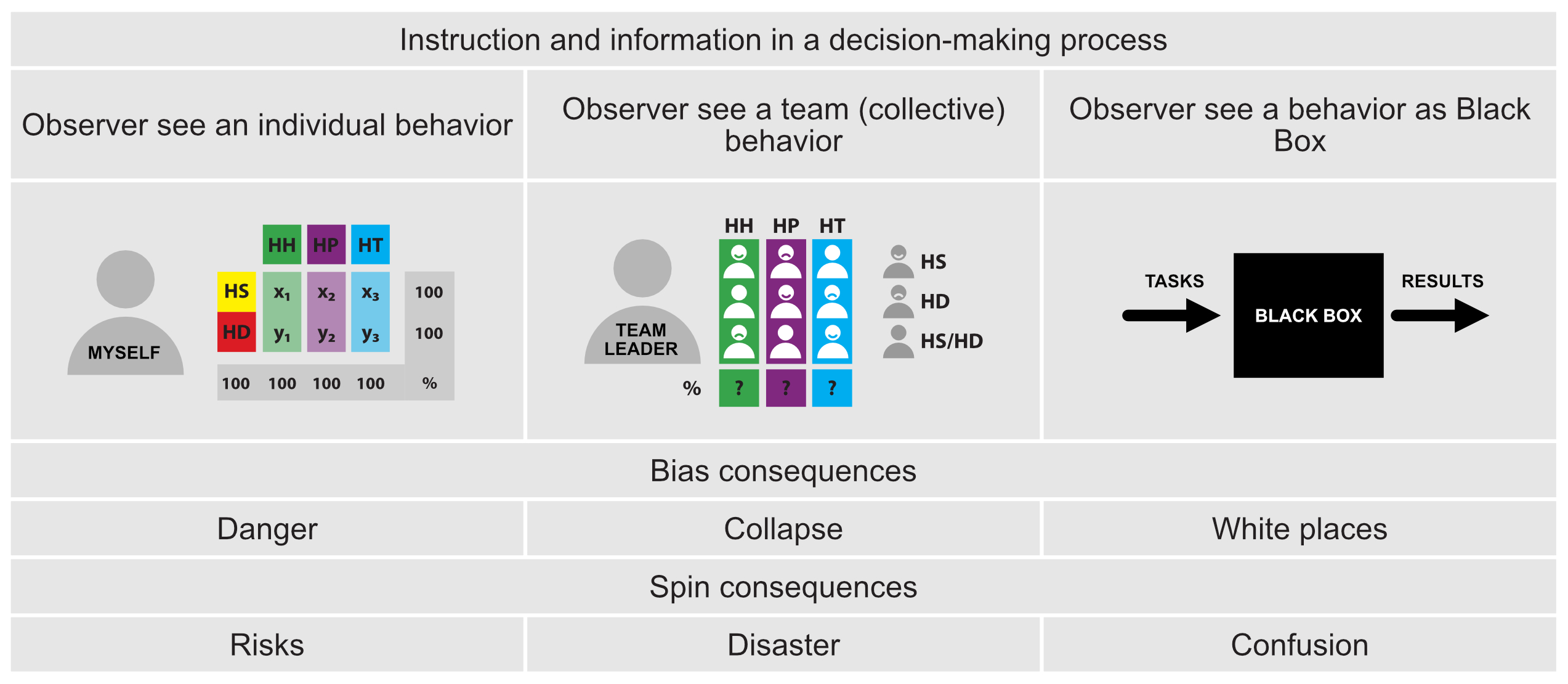
Figure C6g. Bias and spin in a decision-making model
Bias and Consequences
Bias is characterized as stereotypes about people based on their group and immutable physical characteristics, such as gender, ethnicity, or sexual orientation.
This type of bias can have harmful real-world outcomes.
Biases are beliefs not founded on known facts about someone or a particular group of individuals. For example, one common bias is that women are weak (despite many being very strong).
Another is that politicians are dishonest (even when not all) or that subsidies distort the free market (although on the contrary, they can strengthen it).
Unconscious bias can lead to bullying, harassment, discrimination, and feeling excluded, which can bring up a less productive atmosphere in a team or collective.
Bias supports (feeds) the belief that some people, ideas, etc., are better than others. It usually results in mistreating some people, destroying them, destroying teams' work, and the power to change collective positions into dangerous crowd behavior is growing.
One of the most common cognitive biases is confirmation bias. Confirmation bias is when a person looks for and interprets information (be it news stories on the internet, statistical data, or the opinions of others) that backs up an assumption or theory they already have.
Bias is neither inherently good nor bad. Preferences can also come with upsides. Very generally, machines have their "machine learning” and people should have their "behavior improving."
Spin and Consequences
Bias is characterized as stereotypes about people based on their group and immutable physical characteristics, such as gender, ethnicity, or sexual orientation. This type of bias can have harmful real-world outcomes.
Biases are beliefs not founded on known facts about someone or a particular group of individuals. For example, one common bias is that women are weak (despite many being very strong).
Another is that politicians are dishonest (even when not all) or that subsidies distort the free market (although on the contrary, they can strengthen it).
Unconscious bias can lead to bullying, harassment, discrimination, and feeling excluded, which can bring up a less productive atmosphere in a team or collective.
Bias supports (feeds) the belief that some people, ideas, etc., are better than others. It usually results in mistreating some people, destroying them, destroying teams' work, and the power to change collective positions into dangerous crowd behavior is growing.
One of the most common cognitive biases is confirmation bias.
Confirmation bias is when a person looks for and interprets information (be it news stories on the internet, statistical data, or the opinions of others) that backs up an assumption or theory they already have.
Bias is neither inherently good nor bad. Preferences can also come with upsides.
Very generally, machines have their "machine learning” and people should have their "behavior improving."
Figure C6g offers the observer role of changes in objects (e.g., any change in the project and its impact on project stakeholders) due to interventions from any individual or collective decision-making operations. Figure underlines the role and difference between bias effects and spin consequences in time and impact.
Bias is relatively fast, recognizable and measurable. Opposite to this, the Spin is invisible for a long time, and finally, it is speedy and often fatal.
It is called a frog effect: the frog is sitting in a pot of water, and the water is warming; the frog feels nothing for a long time but suddenly is lost, cannot jump up, and is dead.