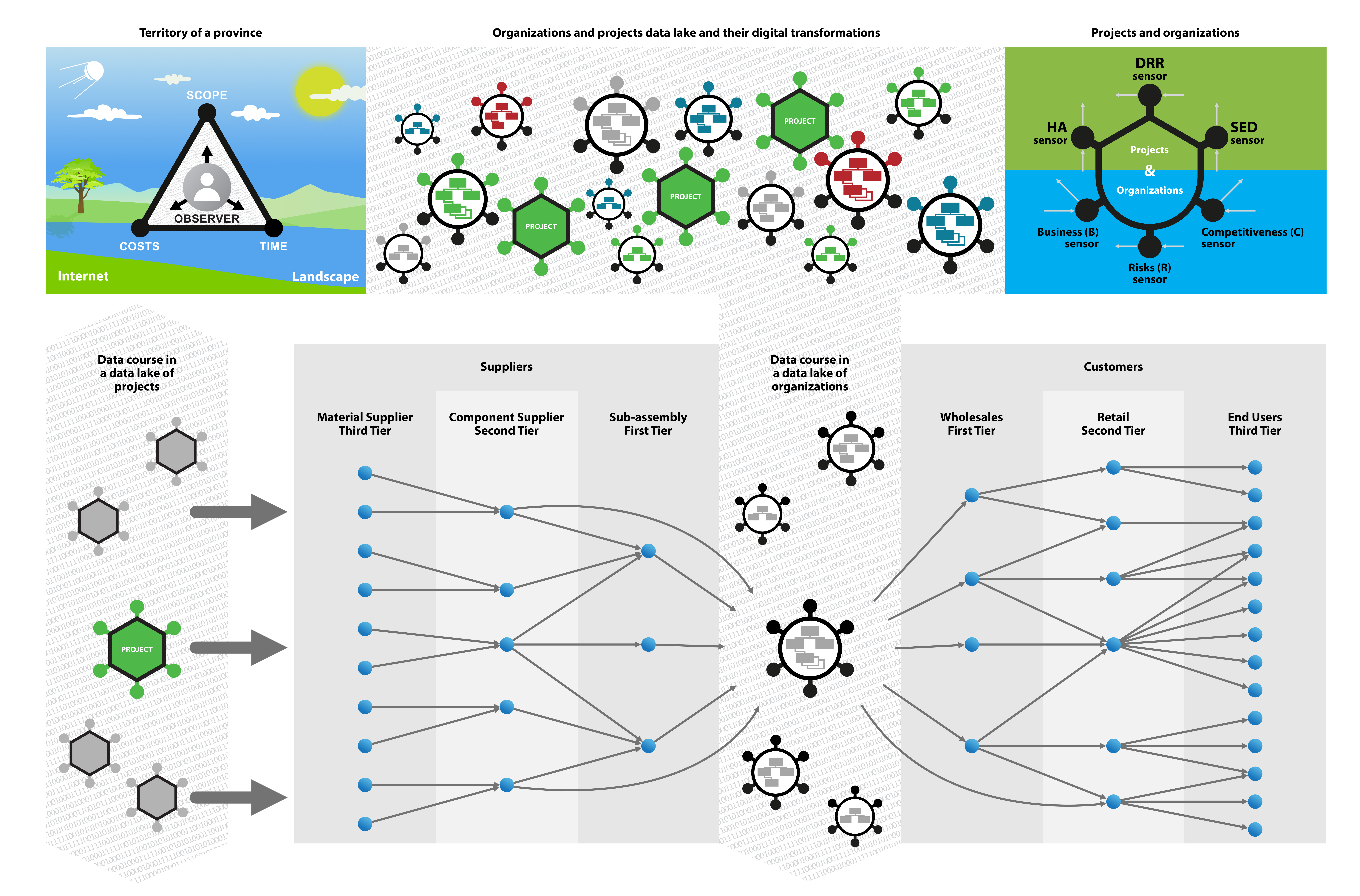
Figure C5c. Organizations and projects are core influencers of the life in a province
Organizations
There are several views on the organization's type, function, size, and mission. If we are looking for the characteristics of an organization that can issue a demand for projects and accepts offers of projects from research and science in the broadest sense, the answer is simple.
We are talking about companies (institutions) in the public sector, enterprises (factories) in the private sector, about non-profit organizations (NGOs).
These organizations are growing with skills to respond meaningfully and independently to the local market's needs and the skills of local public administration. A common feature of these organizations is absorbing new organizational technologies.
The good name of these organizations depends on their success in the local competitive environment and their readiness to enter the global market, of course, first in the place where they operate.
Organization – is the idea of putting things together in a logical order. Generally, it is a group of people who work together. Organizations exist because people working together can achieve more than those working alone. Good organizational skills can make or break a business owner.
It is about competitiveness, profits, and added value for all organizations. Such an approach is ultimately saving you time and reducing stress. A group whose members work in (or for) an organization together for a shared purpose, and in a continuing way, we call a team.
Responsibility
Responsibility of organizations (in a complex of institutions in the public sector, enterprises (factories) in the private sector, and non-profit organizations, NGO) presents two worldwide activities, Environmental, social, and governance (ESG), and Corporate social responsibility (CSR.)
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) conducts research (Consulting) using the various public and private collected information. ESG might conduct research (Consulting) using multiple public and confidential information. ESG might improve a company's ESG behavior through standards development and dissemination for a company's operations that socially conscious investors use to screen potential investments. Environmental criteria consider how a company performs as a steward of nature.
CSR (Common Social Responsibility) is a form of international private business self-regulation that aims to contribute to philanthropic, activist, or charitable, societal goals by engaging in or supporting volunteering or ethically oriented practices. Considered at the organizational level, CSR is, in general, a strategic initiative contributing to a brand's reputation.
Differences:
While ESG is an overall rating of your Company's commitment to sustainability and other values, CSR is your Company's internal commitment to strong corporate values. Think of it this way: good CSR initiatives might help drive high ESG ratings. Both activities have links to UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
Infrastructure (Infrastructure of Human Population)
Infrastructure is a critical, powerful, and common topic of the current era. The population is growing, and waste per capita is growing as well. The waste that both the Human and Nature don't know what to do with it.
The most critical is human waste's multi-functional effects on Nature and the Earth (losses of species of animals and plants, decreasing access to drinking water, clean air, fertile soil, etc.).
In total, the cause of these changes is a fast-expanding infrastructure of the Human that, along with the long-term potential of natural catastrophes (impacts from volcanoes, air and water currents, movement of Earth's crust, soil slides), are causing climate change on the Earth. Generally, the SPC Concept distinguishes large and small infrastructure.
The extensive infrastructure includes technical and societal support and all professional disciplines that the human needs for improvement of quality of his life and his safety (e.g., all workshops, enterprises, their products, services, and impacts of work linked to them).
We include activities related to the sustainability of essential elements of life and human access to them (oil, gas, and water pipeline systems, highways, roads, houses, nature parks, etc.).
Observer role
An observer watches or pays attention to something that can see, hear, or feel. The Great Triad (GT) observer is not an evaluator-discussant critic (someone who prefers discussions).
They should be a renaissance person to absorb information to gain a chance to improve their personality (with a link to one or more of the four theories of intelligence – psychometric, cognitive, social, and physiological).
Their quality is measurable, scalable via added value gained from their personality (e.g., to a product, services, or a performed work), not from their participation in evaluation, criticism, politics, or religion.
Such scaling is not bringing added value from individual cases because it generates (Small Data). These data help different benchmark individual and other (group, collective) opinions. On a large scale (Big Data), are these "discussions" helpful?
The observer role in the GT is essential for understanding the algorithm in distributed (not centralized) organization systems of the open market with goods, services, and works globally. The GT Observer should evaluate three theoretical and three purely pragmatic areas.
The theoretical observations include these relations (polarities):
Philosophy, Love, and Faith.
Philosophy and Science.
Science and Artificial intelligence.
The pragmatic observations include these relations (polarities):
Projects including the new project paradigm and the pleasure of them.
Projects operations stages and technical infrastructure products including gained profits and benefits of them.
Impacts of used and consumed infrastructure on the position of the Human in the GT; well-being, safety, health, and sustainability of life against threats of disasters.
Figure C5c introduces organizations and project objects as the global core influencers on life in a province.
Each territory can have its own "Object-Observer" (composed of unlimited individual observers) that can scale processes, generate data, and build data structures for local needs. Simply sayed, to make (to work) on own local cultural development.
Such observers train each other to be object-oriented in understanding a pool of projects and organizations on their territory. Their interest should be to gain know-how and grasp the supply and demand sides of their territory's critical processes (SED, DRR, and AH projects preparation and implementation).
No one in the global market can buy something like that. It is impossible to import it without the local "Object-Observer" participation. If the "Object-Observer" in a province is missing, any ambition for the Self-Powered Community's success is lost.
It will be multidisciplinary beneficial if more professionals cooperate in the necessary scaling methods development and on the subsequent algorithms (steps) or the applications for the worldwide digital transformation. The aim should keep many emerging digitization projects close together (in space and time).
Accept them as objects for object-programming operations and ensure that their synthesis into purpose-built units is beneficial for widely used practice (timely, operational, and sustainable with sufficient certainty).
Recognizing the role of organizations and projects in the hierarchy of goals in the common framework of sustainability of human existence in the GT is essential for digital transformation.
A practical view of this relationship looks at organizations' products and services. Marketing is clear; people are demanding more and more products and services.
The number and range of functions of various organizations are growing. Likewise, the number and diversity of projects ensuring organizations' success and protection are increasing.
Understanding the role of each (organization and project) in this jungle of data and information is a task that precedes both Global Digital Transformation (GDT) and local initiatives in digitalization (in both developed and developing countries).
A possible way is to scale (look for a purpose for scaling) the impacts of products and services on specific objectives (in the territory, macroeconomics, climate change, and the effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic).
Examples are shown in Figures C5d.1a and C5d.1b, linked to Figures C1c.1 and C1c. It is about the functions of the Human invention (the money tool) in the Great Triad (GT) and the structure of the production of the Human goods in a spectrum of four categories (Private, Common-Pool, Tolls, and Collective interests).
We still see the spectrum as a framework for the Social and Economy Development (SED), Disaster Risks Reduction (DRR), and Humanitarian Aid (HA) projects (as boundaries for the scaling processes).
It is the spectrum of investment strategies, payment mechanisms, and long-time participation in public budgets' debt services on local, national, and global levels.