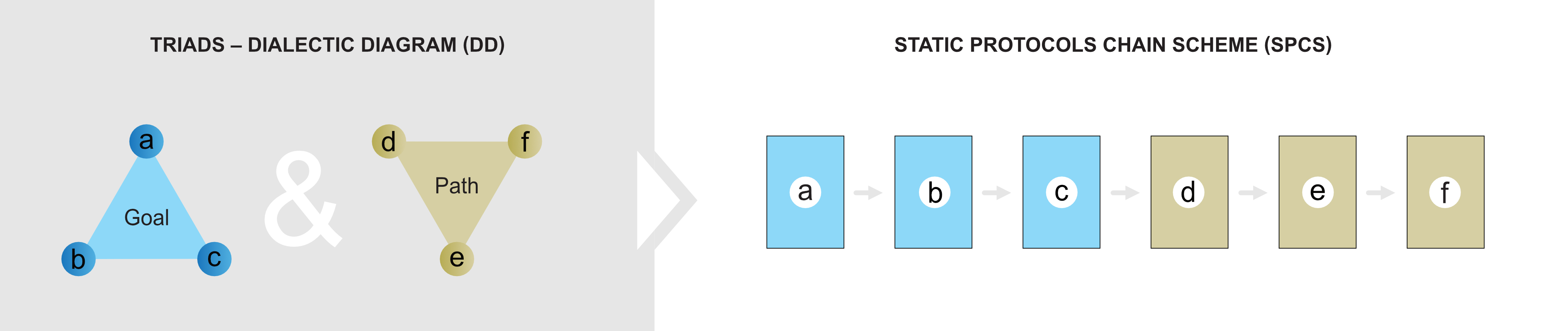
Figure C2c. Triads, linear chain and assumption for scaling
Goal
Common synonyms of goal are aim, design, end, intention, intent, objective, object, and purpose.
While all these words mean "what one intends to accomplish or attain," a goal suggests something attained only by prolonged effort and hardship overcoming.
Path
A path is a trail, route, course, or line of movement.
An example of a long way is what, e.g., deer follow through their movement in a forest (a search of their existence). An example of a short (dynamic) path is a tornado's direction or a deer's way when it is close to the deer female in the rut time.
In this webbook, the triad "Path" represents long and short paths, mainly paths of the Human development and safety effort.
Triad
The world is entering the digital age and breaking down traditional language barriers. So the meta-language (the language of logic symbols) has got a new chance. Shared understanding and common approach depend on precise translations and the main topics for discussion.
Logical signs (e.g., triad, double or bi- triad) support penetration into strategy detail and protect participants of debates against demagogues influences; the goal is to maintain the necessary degree of clarity (transparency) and offer assurance about the discussion's credibility.
Static Protocol
The protocol is a system of rules that explain the correct conduct and procedures to be followed in formal situations.
The protocol can be a plan for a scientific experiment or medical treatment or an informal document describing a treaty or agreement between different sides. Generally, the protocol is a logical system of rules (items) about the correct (supposed) way to act in formal situations.
A static chain of protocols forms items in a row (e. g., the rules for exchanging information between computers) separately concerning the goal of a task and individually to the path to the purpose of the job.
Items of the plan and the way to the destination must not be interconnected if they form a logical chain. Goals and paths to goals have separate internal hierarchies and forms and create, e.g., assumptions for setting priorities.
Figure C2c presents perpartes triads and introduces attributes (protocols) of a chain. It is a linear description of logic protocols respecting the Hexagon structure.