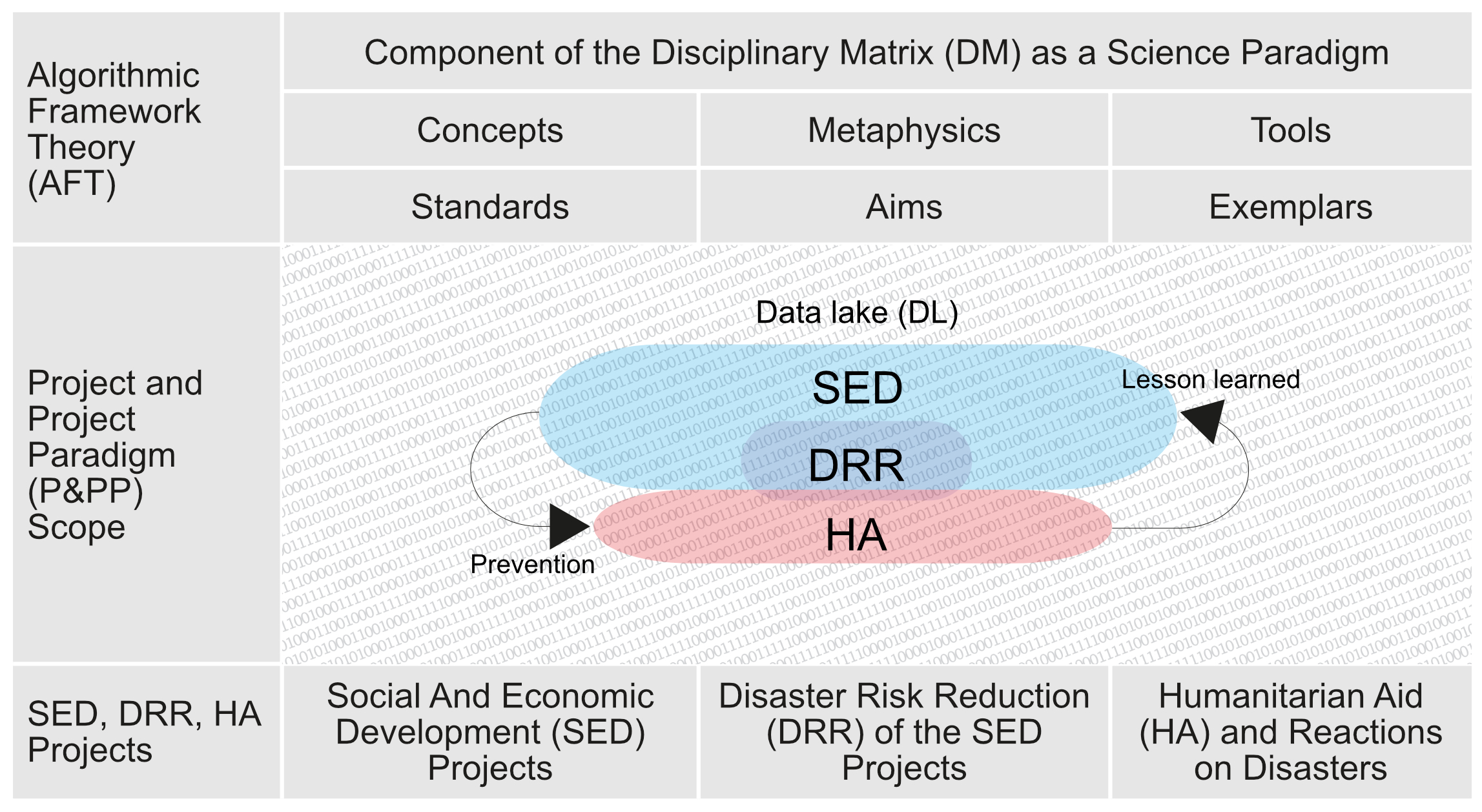
Figure C2a. Science, technique, and Data Lake of SED, DRR, and HA projects
P&S&R
Philosophy, Science, and Research
This summary (according to Wikipedia) is a stimulus on how to think about this chapter. Philosophy is a systematic, rational, and critical examination of reality, the world, and man, including what the world transcends for him (metaphysics), how to be good in it (economics), and to exist (environment).
Philosophy is an intellectual science; it relies on knowledge (it is based on it). Through logical argumentation, philosophy attempts to understand the essence of the Human (both man and woman identity and their connections).
Philosophy fills up religion and motivates culture (each side justifies its values, beliefs, and worldview). Science focuses on natural phenomena, uses empirical data (based on observations or experience), and searches for and applies knowledge and understanding of nature and the social world based on systematic research and evidence.
Such periodic research focuses on describing, explaining, predicting, and controlling observed phenomena. In the Great Triad (GT), the observer is in the role of a researcher. Science confirms his findings' quality, and the philosophy generally seeks suitable knowledge environments for all data obtained. The observer is not an evaluator; observers are objects of the intellectual growth of the Human (see more in Figure C4d).
DM
Disciplinary Matrix
Suppose we simplify the role of the Human for two tasks in a polarity:
Growth of know-how of own sustainability and profitability in the GT environment.
Expansion of financial and capital skills for own sustainability and profitability.
Then we can search if this proposed direction of thinking meets the new requirements for philosophy, science, and research.
Thomas Samuel Kuhn introduced a unique view of science in "The Structure of Scientific Revolutions" (1962). The most critical segment of this book is the "Disciplinary Matrix (DM) of elements in a paradigm." DM covers the work of a scientist, even in the Human role as a philosopher and researcher. Linked to Figure C2a, the DM has six elements (three pairs) with the following mission:
Basic concept - sets the data field and indicates its legal framework.
Standards - defines the relevance and adequacy of selecting problems, their formulation, and evaluation.
Metaphysics - examines the fundamental nature of reality on a broad philosophy level.
Aims – set any internally or externally sorted goals due to Human research (with observer assistance).
Tools – uses tools and instrumentalities, including the theories and standards.
Exemplars – DM concrete on achievements, examples, instantiating laws, concepts, and related standards.
The Kuhnian Disciplinary matrix defines a paradigm as a complex (matrix) of two pairs and six components (Concept, Standards; Metaphysics, Aims; Tools, Exemplars). The concept forms research operations in practical standards to formulate legal, technical, economic, and social feasibility.
Metaphysics (link to the branch of philosophy) defines the fundamental nature of reality, including the relationship between the potentiality and actuality of the relevant object and its aims (including disciplinary goals).
Examples represent specific achievements, specimens, instances, legal environments, concepts, and standards) and are a source for implementing and evaluating benchmarking results in and between different disciplines.
AFT
Algorithmic Framework Theory
Human sustainability and profitability on a scale of the Human living in the Great Triad (GT) and Human ability to keep their tools (money and capital) sustainable and profitable is a task of the economy on all levels - philosophy, science, and research. Li Bin, in his article "The Birth of Unified Economics" (2021), presents "Algorithm Framework Theory (AFT)."
Let me quote some of his thoughts:
According to common sense, economic activities among all kinds of social activities refer to those using or closely relating to money.
Based on the above Algorithmic statements, we can now deem this traditional definition appropriate, which connects economics with or from other social sciences, making a relatively independent domain for economists, allowing them to inherit and innovate.
Any existing method – such as the theoretical, optimistic, normative, statistical, experimental, descriptive, historical, comparative, exemplary, or another-shall continue to be in operations once it is Algorithmically adjusted.
At the same time, economics shall connect closer to other social sciences and humanities, where the unified principles, Algorithmically, bridge all the disciplines concerned.
P&PP
Project & Project Paradigm
A project (according to Google) "is a series of tasks that need to be completed to reach a specific outcome. A project is a set of inputs and outputs to achieve a particular goal. Projects can range from simple to complex and can be achieved by one person, or by hundred ". But in this definition is missing single rules of the project triad: scope of the project, its timing, and all related costs of project preparation and implementation.
Anybody knows that a project has many meanings, but only "Project Management, PM" represents the actual project's genes in a complex and correct present view. PM represents the current project paradigm - a set of universally recognized principles, methodological processes, and cultural concepts that reflect individual regional (continental) schools. There are many perfect PM tools for project preparation and implementation worldwide, and extensive experience and skills exist.
Nevertheless, new ICT technologies, AI apps and products, influences of big data philosophy, and opportunities of new algorithmic theories form a space for the creation of a new project paradigm.
DL
Data Lake
A Data Lake (DL) is presented as a system or repository of data stored in its natural / row format. Usually as object blobs (Binary Large Object) of files. Now DL is presented as a single "large" data store, including raw copies of source system data, sensor data, social, statistics, science, business, and other data.
From, e.g., Wikipedia, we can learn that DL can transform data into tasks (such as reporting, visualization, advanced analytics, and machine learning). The DL can include structured data from a relational database, semi-structured and unstructured data (e-mails, documents, PDFs), and binary data (images, audio, video).
Currently, the main challenge is not creating D.L.s but taking advantage of their opportunities. While present criticisms of DL may be justified, in many cases, they are too general and can be applied to any technological development effort. For example, the "Data Warehouse (D.W.)" technology currently suffers from opacity and changing definitions as DL applications.
Not all data warehouse efforts are successful. Therefore, the Data Lake should be seen as a broader, more comprehensive model of service that provides business value within the production, services, and works matter within the more expansive network of organizations.
Through the DL, the private and public sectors can strengthen the integrity of individual D.L.s and support the efforts of companies and organizations to scale their internal processes and the growth of competition (growing information flow opens the door for the development of competitiveness).
SED
Social and Economy development
If we build an economic development model (ED), social development (SD) cannot stay beside. Therefore, today (in deepening globalization), it only makes sense to talk about social and economic development (SED).
It is one joint sustainable development and security. The modern age brings this value between two stages: the current industrial and post-industrial revolution (we expect a new digital age). The critical tasks of the UN are known:
Stopping wars
Opening business opportunities
Facilitating innovation
Collaborating on research and development (R&D) for SED, DRR, and HA projects
The SED is not only an abbreviation, but also the keyword that will be defined, explained, and commented on in all sections of this webbook in more detail.
DRR
Disaster Risk Reduction
When economic development (ED) and social development (SD) models have a small interface, the growing risks and missing synergy cannot be overlooked.
Therefore, deepening globalization makes sense to talk only about social and economic development (SED), which has a link to the risks of disasters around us. It is one joint and sustainable approach to development and security.
The frequency, quality, and spread of disaster monitoring (e.g., local and global climate change impacts) grow. In parallel, the threats of catastrophic human conflicts are increasing as well.
Therefore, logically the demand for adequate quality and frequency of the measures provided by the DRR projects is growing too. The goal should be to integrate the SED, and DRR approaches to project preparation and implementation and use standard algorithms to standardize these projects further.
The DRR (an abbreviation) will be defined, explained, and commented on in all webbook sections in more detail.
HA
Humanitarian Aid
Humanitarian aid is material and logistical assistance to people and Nature, living and non-living subjects, and objects that need immediate help.
It is usually short-term assistance that, if structured correctly in advance (according to general algorithms for project preparation and implementation), can enrich the know-how of DRR projects and bring important lessons to the preparation and implementation of SED projects.
This webbook deals with the feasibility of the interconnection of SED, DRR, and HA project algorithms. In individual parts, offer new ideas, progressions, and proposals for succeeding.
The HA (an abbreviation) will be defined, explained, and commented on in all webbook sections in more detail.
Super Projects Package (SPP) of tasks (SED, DRR, and HA) is about the quantity and quality of projects. So, the premise of a common view of a super package of tasks (SED, DRR, and HA) is a project.
Project is defined as a summary of partial tasks with the given content and process algorithm that must be prepared and implemented in a set structure of time stages (milestones) and in the spectrum to add volume of funds allocated to each individual project. In this light, the basic characteristics of the SED, DRR, and HA projects can be summarized as follows:
SED: the development of well-being and security of people in their settlements is born through plans with sufficient time reserved for their preparation and implementation. Plan failures are primarily the result of mistakes that people themselves bring to projects.
DRR: the development of well-being and safety of people (e.g., in their residences) is exposed to several risks. DRR projects are looking for the necessary measures and tools to eliminate them or set skills for their management. DRR projects aim to help solve ad hoc situations, prepare SED projects in time, and increase their quality.
HA: It is a quick aid, which must also occur according to the project, although at the beginning of HA, it is more about recording the content of the support, its time description, and the funds consumed (according to the project methodology).
The goal is to save people and their property and gain data. The responsible bodies should do it when it is possible to convert data into a complete project. It will make it possible to transform the acquired data into the know-how of DRR and SED projects in the broader context.
What are the main differences?
SED forms a platform for full-fledged development and application of project algorithms. DRR is a way of recognizing the disaster risks that accompany the preparation, implementation, and use of the new value gained by the project.
Finally, if captured by the methodology of the project algorithm, HA is the actual feedback of improving risk prediction and increasing the quality of development and safety of the human population environment through a standardized projects algorithm with respect to the Great Triad (GT) environment.
What about the philosophy and mathematics in the project processes?
Knowing the pre-set procedures before breaking down the gigantic content of the super package of SED, DRR, and HA into smaller segments is a typical task of interdisciplinary and international cooperation.
It is the content of the challenge of how to penetrate the field of "Big Data, BD" in a fuzzy environment of the "Great Triad, GT". The question is which level starts and how to scale such a significant number of projects and set the potential for common motivation to create work and solve it.
The webbook aims to discuss how to solve this problem by using more philosophy and mathematics. Experts in philosophy, mathematics, and data science have the potential to extend the transparency of this intention and strengthen understanding of the value of the super packages of big data in a fuzzy environment. Some simple tools are discussed in Figure C2b.
What about clusters and the Super Package of the SED, DRR, and HA projects?
Cluster analysis or clustering (according to Wikipedia) is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that they are in the same group (called a cluster) and are more like each other (in a sense) than in other groups (clusters)
It is the main task of exploratory data analysis and a common technique for statistical data analysis used in many areas, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics, and machine learning.
Cluster analysis is not one specific algorithm but a general task that must be solved. It offers various algorithms that differ significantly in understanding what constitutes a cluster and how to find them effectively. Thus, clustering can be a problem in optimizing multiple goals.
There are hundreds of published clustering algorithms worldwide. In summary: There is no objectively "correct" clustering algorithm"; an opinion says that "clustering is in the eye of the beholder."
The most appropriate clustering algorithm for a particular problem often needs an experiment unless there is a mathematical reason to prefer a cluster model. Combining different models is almost impossible. An algorithm designed for one model will generally fail on a data set containing radically different model types.
There are various ways and means to identify, design, and develop data structures and design algorithms. Philosophy and mathematics form a solid basis for further knowledge and application of project packages. The examples indicate in Figure C2b.